What is Configuration mangement? #
- Configuration mangement is the practace of centrally managing and configuring systems from a centralized control point. Configuration management tools are used for remote configuration of systems (Windows or Linux) in an environment.
Configration Management tools #
-
Ansible
-
Puppet
-
Chef
-
SaltStack
About Salt #
-
Started in 2011 by Thomas Hatch
-
Python based, and open source
-
Uses the YAML data structure along with JINJA templating
-
It has a large open source community
-
It uses a client-server model, allowing for remote command execution
-
Easily scalable, supporting thousands of nodes
-
Uses message queue networking
-
Highly modular
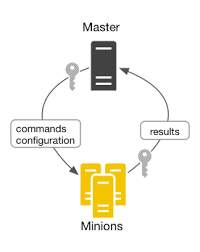
Architecture #
-
Client-server model
- Master (server)
- Minion (client)
-
Uses the asynchronous message library ZeroMQ for message queuing
-
Communication encrypted over SSH
Pillars and Grains #
-
Pillars
- User defined variables that are ctored on the minion
- Also able to be stored on a git server
- User defined variables that are ctored on the minion
-
Grains
- Static information, such as OS version, about a device (minion)
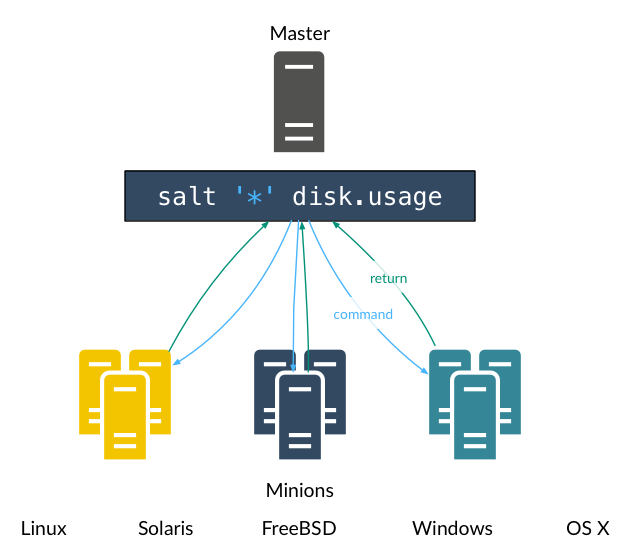
Execution Modules #
- Add hoc commands on the command line targeting one or more minions
States #
-
Each salt state is contained in an Salt State File (SLS)
-
Each state file represents a configuration state that a system should have
-
These state files are written in YAML, and can also contain JINJA templates
network_utilities:
pkg.installed:
- pkgs:
- rsync
- curl
nginx_pkg:
pkg.installed:
- name: nginx
nginx_service:
service.running:
- name: nginx
- enable: True
- require:
- pkg: nginx_pkg
Top File #
- There are two top files that exist
- The states top file maps the machines and the states that should be applied to them
- The pillars top file maps the machines and the pillar data that they can access
base:
# Applied to all servers
'*':
- universal_setp
# Applied only to ubuntu servers
'os:Ubuntu':
- match: grain
- ubuntu_setup
# Applied only to web-server
web-server:
- apache_setup
Targeting Minions #
- We can target minions using a list, regex, grains, or node groups
salt minion1 test.ping
salt "minion*" test.ping
salt -L "minion1, minion2" test.ping
Salt -G 'os_family:windows' test.ping
salt -N windows_minions test.ping
- node groups, configured in master configuration (/etc/salt/master)
nodegroups:
windows_minions 'G@os_family:windows'
Event System #
-
uses publisher/subscribe model for publishing events
-
Events are published onto the event bus and event bus subscribers listen for the published events.
# Watch the event bus forever in a shell while-loop.
salt-run state.event | while read -r tag data; do
echo $tag
echo $data | jq --color-output .
done
Reactor #
- Allows for taking actions related to events by watching the event bus for event tags that match a given pattern and then running one or more commands in response
Installation and Configuration #
Installation (Ubuntu example) #
1. Install the SaltStack repo and key: ```wget -O - https://repo.saltstack.com/apt/ubuntu/18.04/amd64/latest/SALTSTACK-GPG-KEY.pub | sudo apt-key add -``
2. save ```/etc/apt/sources.list.d/saltstack.list``` to ```deb http://repo.saltstack.com/apt/ubuntu/18.04/amd64/latest bionic main```
3. Install the needed Salt components using apt-get
1. salt-master, salt-minion, salt-ssh, salt-api
- Once insalled all Salt components are controlled through systemd unit files
Configuration #
-
salt master: /etc/salt/master
-
Minion: /etc/salt/minion


